Cylindrical vs. Prismatic vs. Pouch Cells: A Comprehensive Battery Comparison
Lithium-ion batteries have become the cornerstone of today’s energy landscape, fueling everything from our everyday smartphones and power station to the cutting-edge electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems driving the green revolution. But what makes these batteries so adaptable, so reliable across such a broad spectrum of applications? The answer lies in their design, and chemistry: cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the structural differences, advantages, and best-fit use cases for each type of lithium-ion cell. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which one suits your needs; whether you’re designing a new product, upgrading a system, or simply curious about the technology that powers the world around us.
What Are the Different Types of Lithium-Ion Battery Cells?
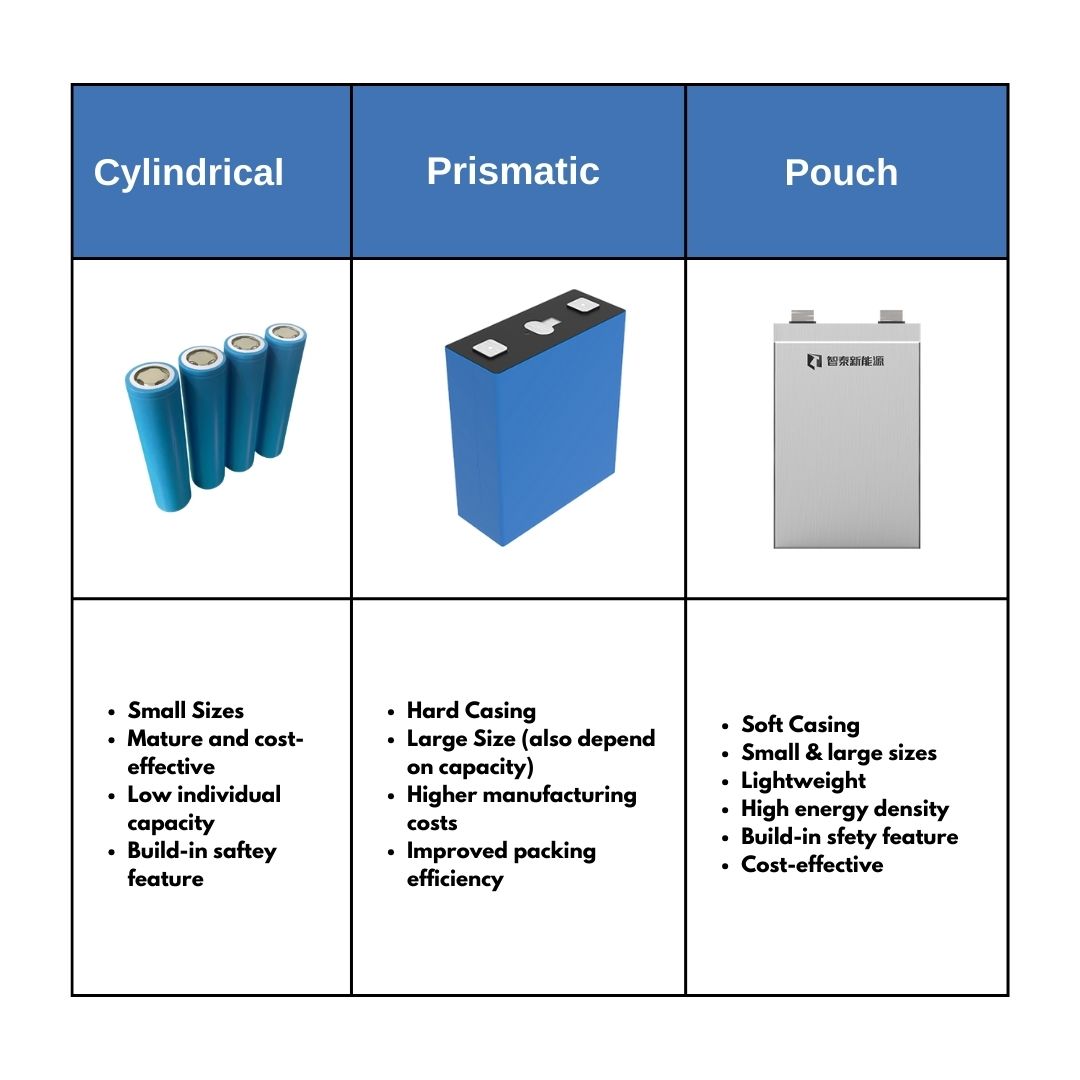
1. Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Battery Cells
Cylindrical cells are the most well-known battery design, commonly seen in devices like power tools, laptops, and electric vehicles. These cells are cylindrical in shape, similar to the size and form of AA batteries, but packed with energy-efficient lithium-ion technology.

Key Characteristics of Cylindrical Cells
- Shape: Round, tubular design, typically encased in a metal can.
- Structure: The electrodes and separator are wound into a tightly-packed spiral, providing a stable internal structure.
- Heat Dissipation: While cylindrical cells have decent heat management, their round shape means they are less space-efficient than prismatic or pouch cells.
Advantages of Cylindrical Cells
- Proven Reliability: These cells have a long history of use, especially in consumer electronics.
- Safety: Cylindrical cells are often considered safer due to their robust casing, which protects against external pressure.
- Easy to Replace: Their standardized shape makes them widely available and easy to replace or swap.
Ideal Uses
Cylindrical cells are often found in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles (EVs), power tools, Energy Storage Systems (ESS), Electric Bicycles and laptops due to their proven efficiency, safety, and reliability.
2. Prismatic Lithium-Ion Battery Cells
Prismatic cells are a popular choice for applications where space efficiency is crucial. They are flat, rectangular cells that can be easily stacked to create dense battery packs. Their unique shape makes them highly customizable for specific devices, from portable electronics to large energy storage systems.

Key Characteristics of Prismatic Cells
- Shape: Flat, rectangular or square design.
- Structure: Electrodes are layered and enclosed in a sturdy metal casing for better mechanical protection.
- Space Efficiency: Their shape allows for tighter packing and greater energy density within the same volume.
Advantages of Prismatic Cells
- Space-Efficient: Ideal for designs where space is limited, such as in smartphones or electric vehicles.
- Heat Management: The flat design allows for better heat dissipation, contributing to improved thermal performance.
- Stackability: They can be easily stacked to create battery packs with higher energy density.
Ideal Uses
Prismatic cells are ideal for, electric vehicles, solar energy storage systems, and portable power stations, BESS, ESS, etc.
3. Pouch Lithium-Ion Battery Cells
Pouch cells, also known as flexible or flat cells, have a distinct soft, flexible casing, unlike the rigid metal casings of cylindrical or prismatic cells. These cells are typically used in applications where weight and space are major concerns, such as in electric vehicles, Energy Storage Systems (ESS), Electric Boats, Portable Power Stations & more.

Key Characteristics of Pouch Cells
- Shape: Flexible, flat, and rectangular or square in shape.
- Structure: They use a lightweight aluminum foil casing and typically have a higher energy density than cylindrical cells.
- Flexibility: The flexible design allows for more versatile integration into compact spaces or curved surfaces.
Advantages of Pouch Cells
- Lightweight: The soft aluminum foil casing reduces the overall weight of the battery.
- High Energy Density: Pouch cells typically offer higher energy density compared to cylindrical cells, making them ideal for devices where power-to-weight ratio is important.
- Customizable Shapes: Their flexible design allows for unique form factors, perfect for tight or irregular spaces.
Ideal Uses
Pouch cells are widely used in Energy Storage Systems (ESS), Electric Bicycles (E-Bikes) and Scooters, electric vehicles (EVs), and electric golf.
Which Battery Type is Right for You?
Choosing between cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch lithium-ion cells depends on your specific needs and application. Here’s a quick guide to help:
- For Electric Vehicles (EVs): Cylindrical cells offer proven performance and safety, making them ideal for EVs.
- For Space-Constrained Applications: Prismatic cells are the best choice for applications where space efficiency and stackability are critical.
- For Lightweight and High-Energy-Density Devices: Pouch cells are ideal for wearables and compact electronics that need high energy in a small, lightweight package.
Conclusion
Cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells all offer distinct advantages depending on your application. Whether you prioritize space efficiency, energy density, or reliability, understanding these differences will help you choose the best battery type for your needs. Keep in mind that the right battery for your project depends not only on performance but also on factors like cost, durability, and ease of integration.
Click here for more Information
Want to Read energy storage system?





